Cloning Interview Questions
What are different type of cloning in Java?
Java supports two type of cloning :-
Deep Cloning
Shallow Cloning
By default shallow clone is used in Java. Object class has a method clone() which does shallow cloning.
What is Shallow copy?
Shallow clone is copying the reference pointer to the object, which means the new object is pointing to the same memory reference of the old object. The memory usage is lower.
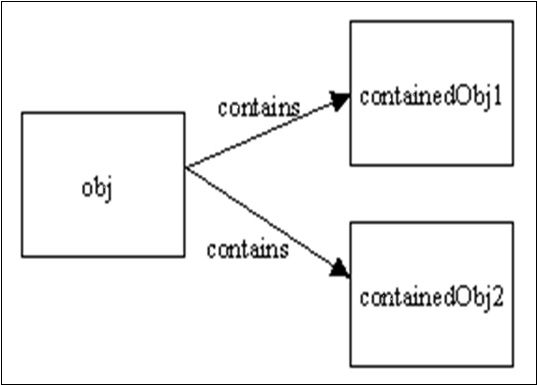
The shallow copy is done for obj and new object obj1 is created but contained objects of obj are not copied.
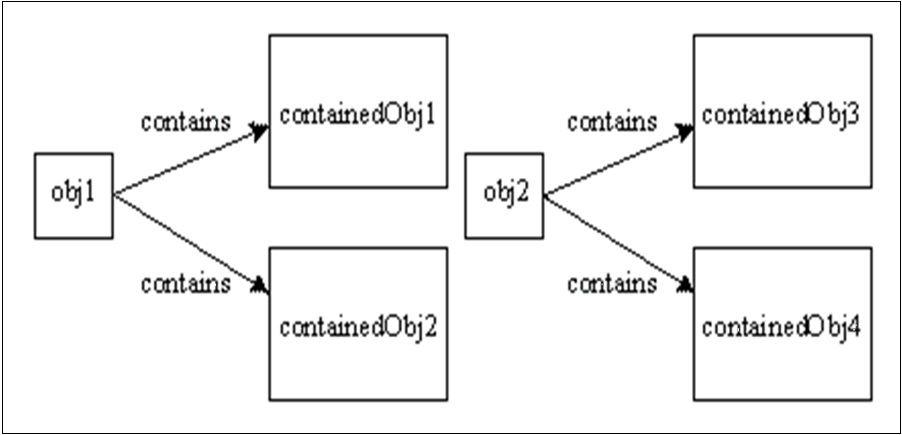
It can be seen that no new objects are created for obj1 and it is referring to the same old contained objects. If either of the contained Obj contain any other object than no new reference is created.
What is difference between deep and shallow cloning?
The differences are as follows :
Consider a class : public class MyData { String id; Map myData; }
The shallow copying of this object will be pointing to the same memory reference as the original object. So a change in myData by either original or cloned object will be reflected in other also.
But in deep copying there will memory allocated and values assigned to the property will be same. Any change in object will not be reflected in other.
Shallow copying is default cloning in Java which can be achieved using Object.clone() method of Object class. For deep copying override the clone method to create new object and copy its values.
What are disadvantages of deep cloning ?
Disadvantages of using Serialization to achieve deep cloning :-
Serialization is more expensive than using object.clone().
Not all objects are serializable.
Serialization is not simple to implement for deep cloned object.