Database Views Introduction
Views
Views are a logical entity which act as a mask on the table.
Views will be created based on the table by fetching the data from the table, but the view does not contain the data physically. When view needs the data, it will get it from the table.
Syntax:
Create view view_name Select statement;
Query:
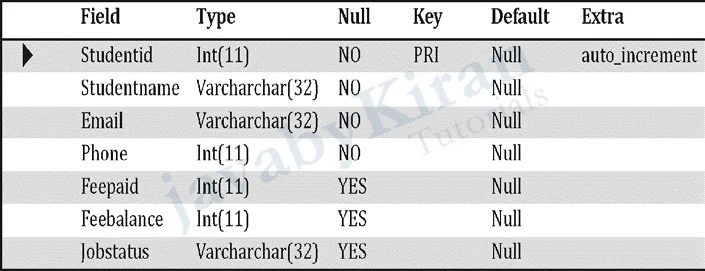
create table students(
studentid int primary key auto_increment not null, studentname varchar(32) not null,
email varchar(32) not null, phone int not null,
feepaid int, feebalance int, jobstatus varchar(32));
Role:
-
admin mg - email, phone
Account mgr - Student ID, Fee Paid, Fee Balance
HR mgr - Student ID, Student name, email, phone, job status
Admin_view:
create view admin as
select email

Account_view:
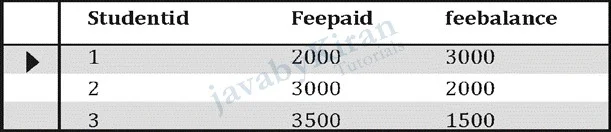
create view accountmanager as
select studentid, feepaid, feebalance from students;
HR_View:
select studentid, studentname, email, phone, jobstatus from students;
Advantages:
Increase the security levels
Decreases redundancy
Views Types
Types:
Static views
Dynamic views
Static Views:
Static views also called as read only views
We cannot perform insert, update and delete operations on static views
Dynamic Views:
Dynamic views are also called updatable views
You can perform select, insert, update and delete operations on the updatable views or in the dynamic views
| Sr. No | Select state of view | Static View | Dynamic View |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contains primary key | - | . |
| 2. | Does not contain a primary key | . | - |
| 3. | Contains aggregate functions | . | - |
| 4. | Does not contain agg format | - | . |
| 5. | Contains group by | . | - |
| 6. | Does not contain group by | - | . |
| 7. | Contain joins | . | - |
| 8. | Does not contain join | - | . |
Example
Example:
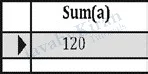
create table hello(id int primary key auto_increment not null,a int, b int, c int);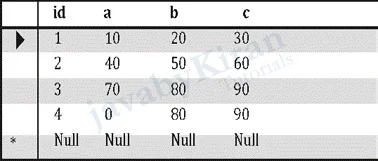
create view v1 as
select sum(a) from hello;