Variable Initialization, Declaration and Casting
Syntax of Variable Declaration
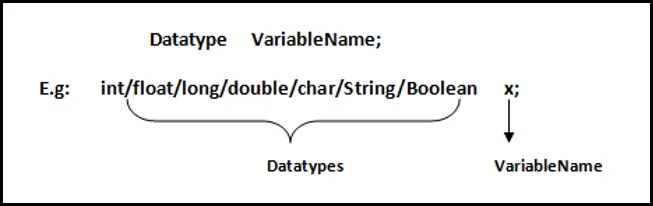
How to Declare Variable?
Integer
This group includes byte, short, int, long.
byte : It is 8 bit (1 byte) integer data type. Value range from -128 to 127. Default value zero.
example:byte b=10;short : It is 16 bit (2 byte) integer data type. Value range from -32768 to 32767. Default value zero.
example:short s=11;int : It is 32 bit (4 byte) integer data type. Value range from -2147483648 to 2147483647. Default value zero.
example:int i=10;long : It is 64 bit (8 byte) integer data type. Value range from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. Default value zero.
example:long l=100012;
Floating-Point Number
This group includes float, double.
float : It is 32 bit (4 byte) float data type. Default value 0.0f
example:float ff=10.3f;double : It is 64 bit (8 byte) float data type. Default value 0.0d
example:double db=11.123;
Characters
This group represent char, which represent symbols in a character set, like letters and numbers.
char : It is 16 bit (2 byte) unsigned unicode character. Range 0 to 65,535
example:char c='a';
Boolean
This group represent boolean, which is a special type for representing true/false values. They are defined constant of the language.
example:boolean b=true;
How to Initialize Variable?
Datatype VariableName = Value;
example: int a=10;
Type Casting
Assigning a value of one type to a variable of another type is known as Type Casting.
Example :
int x = 10;
byte y = (byte)x;
In Java, type casting is classified into two types,
Widening Casting (Implicitly done)

Narrowing Casting (Explicitly done)

Widening or Automatic type conversion
Automatic Type casting takes place when,
The two types are compatible.
The target type is larger than the source type.
Example
package com.javabykiran.variablesdemo;
public class JbkTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 100;
long l = i; // no explicit type casting required
float f = l; // no explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Int value " + i);
System.out.println("Long value " + l);
System.out.println("Float value " + f);
}
}
Output:
Int value 100
Long value 100
Float value 100.0